As we know, there are certain basic operations that we frequently perform on a data structure to meet our requirements. In this tutorial, we will learn how to perform these basic operations with the Array data structure.
First, we will discuss the different types of basic operations:
Insert: - Adding a new element to the array.
Search: - Finding an element in the array.
Delete: - Removing an element from the array.
Update: - Modifying an existing element in the array.
Select: - Retrieving an element from the array.
Sort: - Arranging the elements of the array in a specified order.
Insert Operation: This involves adding an element to the array. With the Array data structure, we can encounter different scenarios for the insert operation:
a. Add the element at the beginning of the array.
b. Add the element at the end of the array.
c. Add the element at a specified position in the array.
• Create a new array with a length of given_array_length + 1.
• Store the given element at the 0th index of the newly created array.
• Copy all elements from the old array (from the 0th to the last index) to the newly created array, starting from index 1.
• Print the newly created array to verify the result.
class JTC{
public static void main(String arg[]){
// Creating a Static Array
int[] ar1 = {101,202,303,404,505};
// Traversing the Array from 0th Index to Last Index
for(int i = 0; i <= ar1.length-1; i++){
System.out.println("Index :- "+i+" | Value :- "+ar1[i]);
}
}
}
75 11 -56 23 67 90
In this example, we demonstrate how to insert a new element at the beginning of a given array.We have a class named JTC, which contains a method: static int[] insertAtBeginning(int[] ar1, int value) This method is designed to insert an element at the beginning of the provided array. The method takes two arguments: the array ar1 and the value to be inserted. It then returns the resulting array to the caller.
• Create a new array with a length of given_array_length + 1.
• Copy all elements from the old array (from the 0th to the last index) to the newly created array.
• Store the given element at the last index of the newly created array.
• Print the newly created array to verify the result.
class JTC{
static int[] insertAtEnd(int[] ar1, int value){
// Creating an new array.
int[] new_array = new int[ar1.length+1];
// storing all the elements of old array into the newly created array.
int i = 0;
while(i <= ar1.length-1){
new_array[i] = ar1[i];
i++;
}
// storing value at the last index of the newly created array.
new_array[i] = value;
return new_array;
}
public static void main(String arg[]){
int[] ar1 = {-11,23,56,34,90};
int[] result = insertAtEnd(ar1, 67);
for(int i = 0; i <= result.length-1; i++){
System.out.print(result[i]+" ");
}
}
}
-11 23 56 34 90 67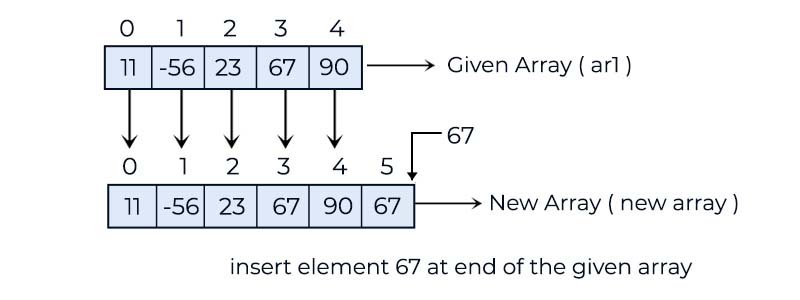
In this example, we demonstrate how to insert a new element at the end of a given array. We have a method: static int[] insertAtEnd(int[] ar1, int value)inside the JTC class, which is dedicated to adding the value at the last index position of the ar1 array.
• Create a new array with a length of given_array_length + 1.
• Copy all elements from the 0th index to the specified index from the old array to the newly created array.
• Store the given element at the specified index of the newly created array.
• Copy the remaining elements from the old array into the newly created array, starting from the index immediately after the specified index.
• Print the newly created array to verify the result.
class JTC{
static int[] insertAtPosition(int[] ar1, int index, int value){
int[] new_array = new int[ar1.length+1];
int i = 0;
while(i <= index-1){
new_array[i] = ar1[i];
i++;
}
new_array[i] = value;
i++;
for(int j = i; j <= new_array.length-1; j++){
new_array[j] = ar1[j-1];
}
return new_array;
}
public static void main(String arg[]){
int[] ar1 = {-23,56,24,678,23,-11,0,35};
int[] result = insertAtPosition(ar1,3,56);
for(int i = 0; i <= result.length-1; i++){
System.out.print(result[i]+" ");
}
}
}
-23 56 24 56 678 23 -11 0 35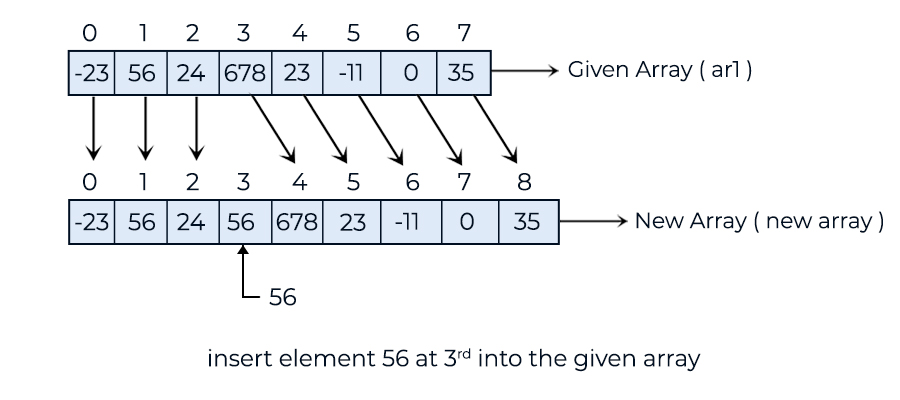
In this example, we demonstrate how to insert an element at a specified index in a given array.We have a method: static int[] insertAtPosition(int[] ar1, int index, int value)Which is designed to insert the given value into the ar1 array at the specified index. The method then returns the resultant array.
In this section of the article, we will understand how to search for an element in a given Array data structure.
To perform a search operation on an array data structure, follow these steps:
• Traverse the array from the 0th index to the last index position.
• In each iteration, compare the given element with the element at the current index of the array.
class JTC{
static void search(int[] ar1, int value){
boolean status = false;
int i = 0;
for(i= 0; i <= ar1.length-1; i++){
if(ar1[i] == value){
System.out.println(value+" found at "+i+" index.");
break;
}
}
if(i == ar1.length){
System.out.println(value+" not found.");
}
}
public static void main(String arg[]){
int[] ar1 = {101,202,303,404,505};
search(ar1,303);
search(ar1,-97);
}
}
303 found at 2 index.
-97 not found.
In this example, we demonstrate how to search for a given element in an array. As shown, there is a method: int search(int[] ar1, int value) which is dedicated to searching for the specified element in the given array.
In this part of the article, we will understand how to delete an element from a given array.
There are four different scenarios for performing a delete operation on an array:
a. Delete the first element from the given array.
b. Delete the last element from the given array.
c. Delete the element at a specified position from the array.
d. Delete a specified element from the given array.
Approach 1:
• Traverse the array starting from the 1st index to the last index position.
• Copy each element from the current index to the previous index.
• Traverse the array from the 0th index to the second-to-last index and print the values.
class JTC{
static void delete(int ar1[]){
for(int i = 1; i <= ar1.length-1; i++){
ar1[i-1] = ar1[i];
}
for(int i = 0; i <= ar1.length-2; i++){
System.out.print(ar1[i]+" ");
}
}
public static void main(String arg[]){
int[] ar1 = {101,202,303,404,505};
delete(ar1);
}
}
202 303 404 505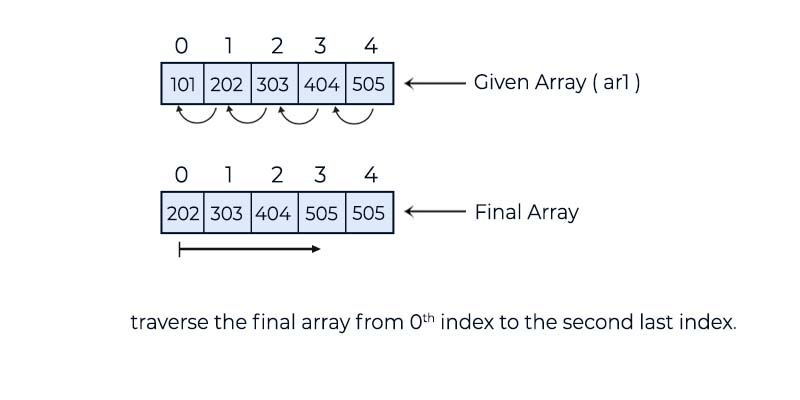
In this example, we demonstrate how to delete the first element from a given array. As shown, we have a delete method specifically designed to remove the element at the first index position of the array.
Approach 2:
• Create a new array with a length equal to old_array_length - 1.
• Copy elements from the 1st index of the old array to the newly created array, continuing until the last element
• Traverse the newly created array from the 0th index to the last index and print the values.
class JTC{
static void delete(int ar1[]){
// creating new array.
int[] new_array = new int[ar1.length-1];
// copy element from 1st index of old array to the new array.
for(int i = 1; i <= ar1.length-1; i++){
new_array[i-1] = ar1[i];
}
// Traversing Array to print the new array element.
for(int i = 0; i <= new_array.length-1; i++){
System.out.print(new_array[i]+" ");
}
}
public static void main(String arg[]){
int[] ar1 = {101,202,303,404,505};
delete(ar1);
}
}
202 303 404 505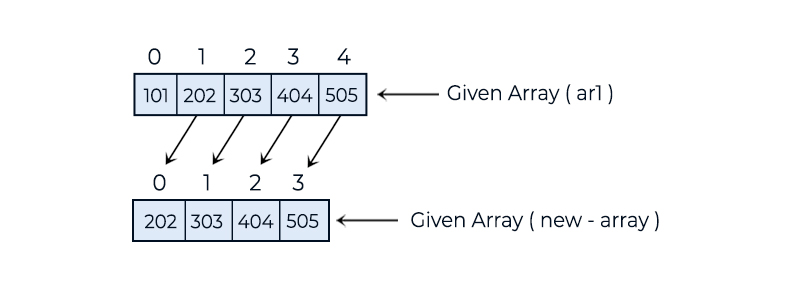
In the above example, we demonstrate how to delete the data from the first index position of a given array using a new array.
• Create a new array with a length equal to old_array_length - 1.
• Copy all elements from the old array to the new array, stopping at the second-to-last element.
• Traverse the new array and print its elements.
class JTC{
static void delete(int ar1[]){
// creating new array.
int[] new_array = new int[ar1.length-1];
// copy element from 1st index of old array to the new array.
for(int i = 0; i <= ar1.length-2; i++){
new_array[i] = ar1[i];
}
// Traversing Array to print the new array element.
for(int i = 0; i <= new_array.length-1; i++){
System.out.print(new_array[i]+" ");
}
}
public static void main(String arg[]){
int[] ar1 = {101,202,303,404,505};
delete(ar1);
}
}
101 202 303 404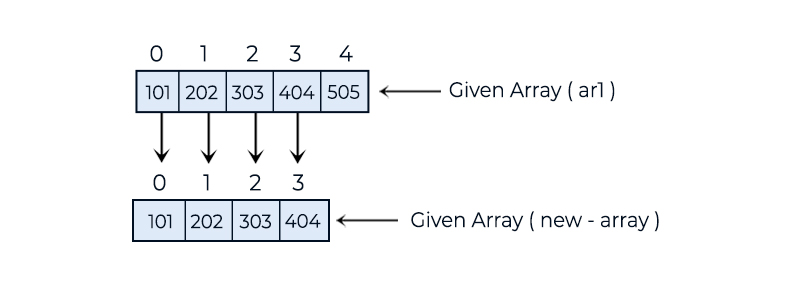
• Create a new array with a length equal to old_array_length - 1.
• First, copy the elements from the 0th index to given_position - 1 from the old array to the new array.
• Then, copy the elements from the given_position to the last index of the old array into the new array.
• Traverse the newly created array and print its elements.
class JTC{
static void delete(int[] ar1, int pos){
int[] new_array = new int[ar1.length-1];
for(int i = 0; i < pos-1; i++){
new_array[i] = ar1[i];
}
for(int i = pos; i <= ar1.length-1; i++){
new_array[i-1] = ar1[i];
}
for(int i = 0; i <= new_array.length-1; i++){
System.out.print(new_array[i]+" ");
}
}
public static void main(String arg[]){
int[] ar1 = {101,202,303,404,505,606};
delete(ar1,3);
}
}
101 202 404 505 606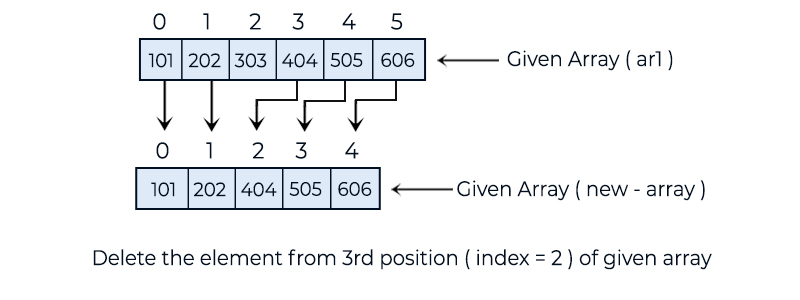
In the above example, we have a given array int[] ar1 = {101, 202, 303, 404, 505, 606}; and the delete position is 3. In the delete method, we create a new array int[] new_array = new int[ar1.length - 1]; and then copy the data from the given array to the newly created array using two for loops. Finally, we use a for loop to print the elements of the new array on the console.
• First, find the position of the given element in the array.
• Create a new array with a length equal to old_array_length - 1.
• Copy elements from the 0th index to given_position - 1 from the old array to the new array.
• Then, copy elements from given_position + 1 to the last index of the old array into the new array.
• Traverse the newly created array and print its elements.
class JTC{
static void delete(int[] ar1, int element){
int pos = -1;
for(int i = 0; i <= ar1.length-1; i++){
if(ar1[i] == element){
pos = i+1;
break;
}
}
if(pos != -1){
int[] new_array = new int[ar1.length-1];
for(int i = 0; i < pos-1; i++){
new_array[i] = ar1[i];
}
for(int i = pos; i <= ar1.length-1; i++){
new_array[i-1] = ar1[i];
}
for(int i = 0; i <= new_array.length-1; i++){
System.out.print(new_array[i]+" ");
}
}else{
System.out.println("element not found");
}
}
public static void main(String arg[]){
int[] ar1 = {101,202,303,404,505,606};
delete(ar1,505);
}
}
101 202 303 404 606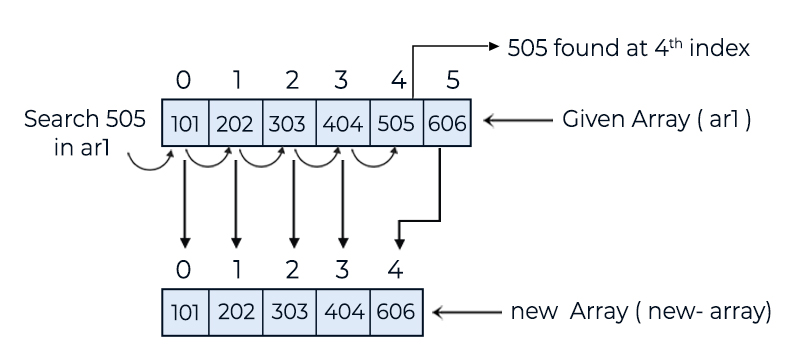
In this example, we demonstrate how to delete a specified element from a given array. In the delete() method, we first find the position of the given element in the array. Then, using a new array, we remove the specified element from the original array.
In this section, we will discuss the update operation, which involves searching for an element in the array and updating it with a new value.
There are two different scenarios for the update operation:
a. Search for the given element in the array and update the first occurrence of the element with a new value.
b. Search for the given element in the array and update all occurrences of the element with a new value.
• Traverse the array from the 0th index to the last index to search for the given element.
• If the element is found, break the loop and update it with the new value.
• Traverse the updated array to print the results.
class JTC{
static void update(int[] ar1, int element, int new_element){
String pos = "";
// Finding the given element into the given array.
for(int i = 0; i <= ar1.length-1; i++){
if(ar1[i] == element){
ar1[i] = new_element;
break;
}
}
// Traversing the updated Array.
for(int i = 0; i <= ar1.length-1; i++){
System.out.print(ar1[i]+" ");
}
}
public static void main(String arg[]){
int[] ar1 = {101,202,303,404,505};
update(ar1,303,-90);
}
}
101 202 -90 404 505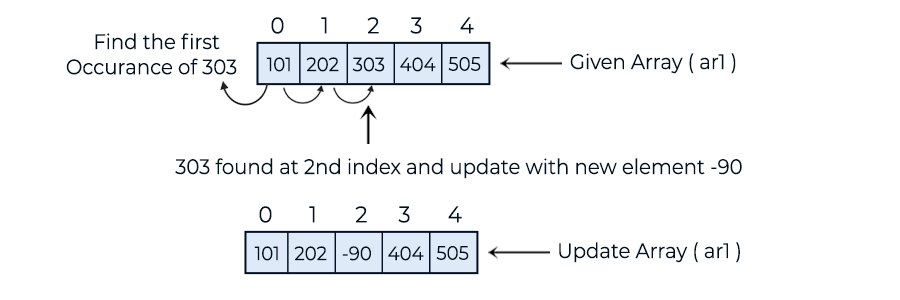
In the above example, we have a method update(int[] ar1, int element, int new_element) that is dedicated to searching for a given element in the array and updating it with a new value.Inside the update method, a for loop traverses the array from the 0th index to the last index. If the specified element is found, it is updated with the new value.
Finally, another for loop traverses the updated array from the 0th index to the last index and prints the values to the console.
• Traverse the array from the 0th index to the last index to search for the given element.
• If the element is found, update it with the new value.
• Finally, traverse the updated array to print the results.
class JTC{
static void update(int[] ar1, int element, int new_element){
String pos = "";
// Finding the given element into the given array.
for(int i = 0; i <= ar1.length-1; i++){
if(ar1[i] == element){
ar1[i] = new_element;
}
}
// Traversing the updated Array.
for(int i = 0; i <= ar1.length-1; i++){
System.out.print(ar1[i]+" ");
}
}
public static void main(String arg[]){
int[] ar1 = {101,202,303,404,303,505,303,606};
update(ar1,303,-90);
}
}
101 202 -90 404 -90 505 -90 606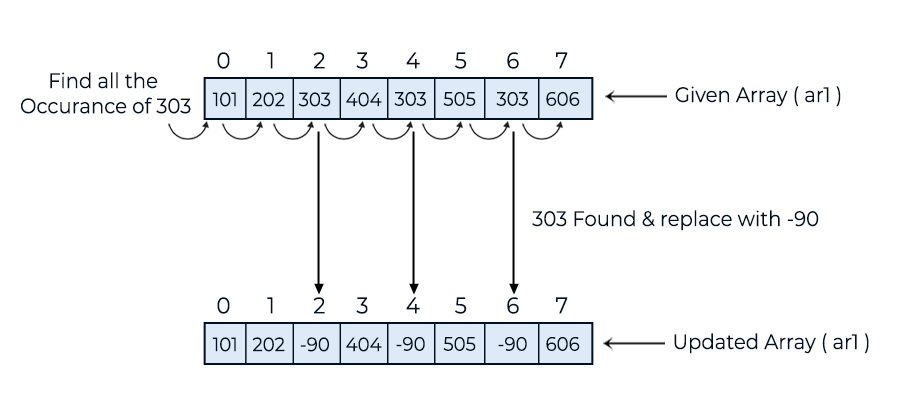
In this example, we find all occurrences of the given element in the array and update them with the new value.
In this section, we will learn how to retrieve elements from an array based on business logic.
We will practice the selection operation on arrays with a few use cases:
a. Print all elements from the array in forward direction.
b. Print all elements from the array in reverse order.
c. Print all elements of the array that are prime numbers.
class JTC{
// printing the element in forward order.
static void forward(int[] ar1){
System.out.println("In forward order :- ");
for(int i = 0; i <= ar1.length-1; i++){
System.out.print(ar1[i]+" ");
}
}
// printing the element in reverse order.
static void reverse(int[] ar1){
System.out.println("\nIn reverse order :- ");
for(int i = ar1.length-1; i >= 0; i--){
System.out.print(ar1[i]+" ");
}
}
// printing only prime number.
static void prime(int[] ar1){
System.out.println("\nPrime Elements only :- ");
for(int i = 0; i <= ar1.length-1; i++){
int num = ar1[i];
if(num > 0){
int status = 0;
for(int j = 2; j <= num/2; j++){
if(num % j == 0){
status = 1;
break;
}
}
if(status == 0){
System.out.print(ar1[i]+" ");
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String arg[]){
int[] ar1 = {101,202,303,404,505};
forward(ar1);
reverse(ar1);
prime(ar1);
}
}
In forward order :-
101 202 303 404 505
In reverse order :-
505 404 303 202 101
Prime Elements only :-
101In this example, we have three different methods: forward(int[] ar1), reverse(int[] ar1), and prime(int[] ar1), each designed to handle array elements differently.
The forward(int[] ar1) method prints the array elements in a forward direction. It utilizes a for loop to traverse the array from the 0th index to the last index, printing each element to the console.
On the other hand, the reverse(int[] ar1) method prints the array elements in reverse order. This method uses a for loop to start at the last index and move towards the 0th index, printing each element as it goes.
Lastly, the prime(int[] ar1) method focuses on printing only the prime numbers from the array. It also uses a for loop to traverse the array from the 0th index to the last index. For each element, it checks if the element is a prime number and prints it to the console if it is.
In this section, we will learn how to sort or arrange the array elements into a specific order.
We will understand the sort operation using two general use-cases:
a. Sort the array in ascending order.
b. Sort the array in descending order.
• Traverse the array from the 0th index to the last index.
• Compare each element with the remaining elements.
• If the current element is greater than the next element, swap their positions.
• Finally, traverse the array in the forward direction and print the elements to the console.
class JTC{
static void ascending(int[] ar1){
// traversing the array in forward direction.
for(int i = 0; i <= ar1.length-1; i++){
// traversing the remaining elements of the array.
for(int j = i+1; j <= ar1.length-1; j++){
// comparing current_element > next_element
if(ar1[i] > ar1[j]){
// swaping current_element and next_element position.
int swap = ar1[i];
ar1[i] = ar1[j];
ar1[j] = swap;
}
}
}
// printing the array element in forward direction.
for(int i = 0; i <= ar1.length-1; i++){
System.out.print(ar1[i]+" ");
}
}
public static void main(String arg[]){
int[] ar1 = {10,-9,45,3,56,89};
ascending(ar1);
}
}
-9 3 10 45 56 89In this example, we have a method `ascending(int[] ar1)` that sorts the array elements in ascending order. Within the `ascending()` method, there is a `for` loop `for (int i = 0; i <= ar1.length - 1; i++)` which traverses the array from the 0th index to the last index. Inside this loop, there is a nested `for` loop `for (int j = i + 1; j <= ar1.length - 1; j++)` dedicated to traversing the remaining elements of the array. During each iteration of the inner loop, we compare the current element with the next element using `if (ar1[i] > ar1[j])`. If the current element is greater than the next element, we swap their positions. Finally, another `for` loop `for (int i = 0; i <= ar1.length - 1; i++)` is used to print the sorted array elements to the console.
• Traverse the array from the 0th index to the last index.
• Compare each remaining element with the current element.
• If the current element is less than the next element, swap their positions.
• Finally, traverse the array in forward direction and print its elements to the console.
class JTC{
static int[] insertAtEnd(int[] ar1, int value){
// Creating an new array.
int[] new_array = new int[ar1.length+1];
// storing all the elements of old array into the newly created array.
int i = 0;
while(i <= ar1.length-1){
new_array[i] = ar1[i];
i++;
}
// storing value at the last index of the newly created array.
new_array[i] = value;
return new_array;
}
public static void main(String arg[]){
int[] ar1 = {-11,23,56,34,90};
int[] result = insertAtEnd(ar1, 67);
for(int i = 0; i <= result.length-1; i++){
System.out.print(result[i]+" ");
}
}
}
89 56 45 10 3 -9In this example, we have a method descending(int[] ar1) which sorts the array elements in descending order. In the descending() method, there is a for-loop for(int i = 0; i <= ar1.length - 1; i++) {} that traverses the array from the 0th index to the last index. Inside this for-loop, there is a nested for-loop for(int j = i + 1; j <= ar1.length - 1; j++) {} dedicated to traversing the remaining elements of the array. In each iteration of the inner for-loop, we compare the current element with the next element if(ar1[i] < ar1[j]) {}. If the current element is less than the next element, we swap their positions. Finally, there is another for-loop for(int i = 0; i <= ar1.length - 1; i++) {} that is used to print the array elements to the console.