• When you send the request using the HTTP protocol, that request is called an HTTP request.
• HttpRequest containes two parts.
o HttpServletHeaders.
o HttpRequest Body.
• When you send the request with the HTTP method Get, the first parameter data will be converted to Query String, and that query string will be attached to the URL as follows:
http://loacalhost:9999/Jtc1/login.html
http://loacalhost:9999/Jtc1/login.jtc?username=som&password=jtcindia
| http://localhost:9999/Jtc1/login.jtc | URL |
| /Jtc1 | CONTEXT PATH |
| http | PROTOCOL |
| Localhost | HOST |
| 9999 | PORT |
| /Jtc1/login.jtc | URL |
| Username=som&password=jtcindia | Query String |
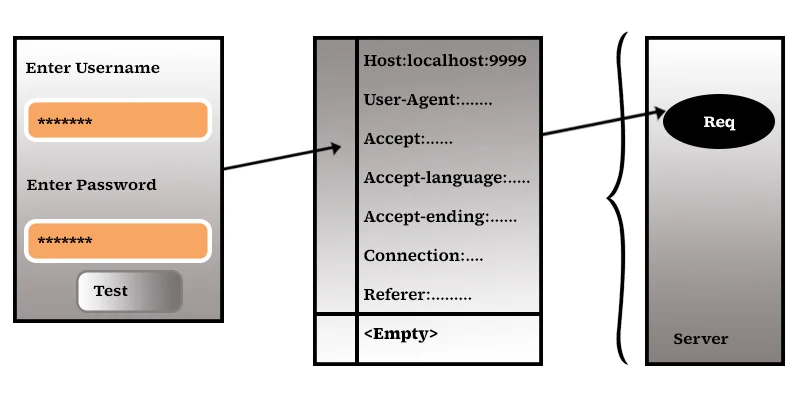
In this case, the HTTP method GET. This data will be placed in HttpRequest Headers, and the HttpRequest Body is empty.
http://loacalhost:9999/Jtc1/login.jtc?username=som&password=jtcindia
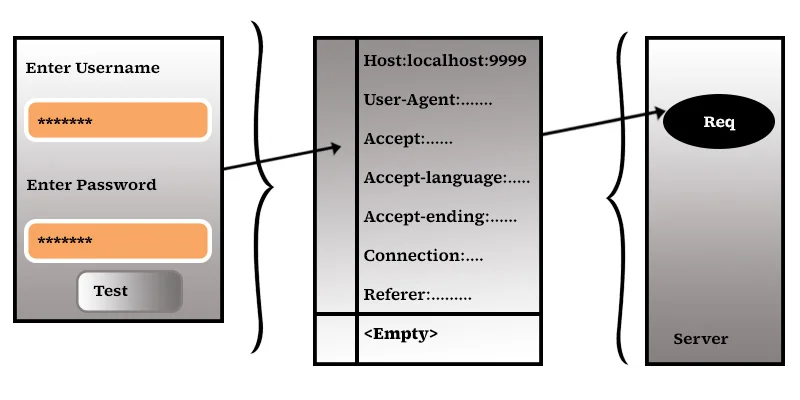
When you send the request with the HTTP method POST, the parameter data will be converted to a query string, and that query string will be placed in the Httprequest body. Then URL is like
http://loacalhost:9999/Jtc1/login.jtc?username=som&password=jtcindia
| GET | POST |
|---|---|
| When you send the request with Http method GET. This data will be attached to URL as Query String. | When you send the request with Http method POST, this data will be placed in HttpRequest Body. |
| Using GET, you can send only limited amount of Data. | Using POST, you can send unlimited amount of data. |
| GET is not secure because data will be visible in the URL | POST is more secure |
• On the server side, Container is responsible for creating HttpServletRequest and HttpServletResponse objects and initialising those objects with the data.
• HttpServletRequest contains the followings information
o Request parameters
o Request Headers
o Request Cookies
o Other Information.
• HttpServletResponse contains the bytes and characters.
o Response Headers.
o Response stream in terms of bytes and characters.
Files Required for Program
1. Index.html
2. TestServlet.java
3. Web.xml
1. Index.html
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=ISO-8859-1">
<title>Insert title here
</head>
<body>
<center>
<h1>Request & Response Example</h1>
</center>
<form action="test.jtc" method="post">
<h2>Enter Uname</h2>
<br>
<input type="text" name="uname" />
<h2>Enter Password</h2>
<input type="password" name="password" />
<br>
<input type="submit" value="Test" />
</form>
</body>
</html>
2. TestServlet.java
package com.jtcindia.servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import
javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class TestServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res) throws
ServletException, IOException {
//1. Request parameters
String un = req.getParameter("uname");
String
pw = req.getParameter("password");
//2. display request parameters
PrintWriter out = res.getWriter();
out.println("<h1>Username:" + un);
out.println("<br>Password:" + pw);
out.println("<br>");
out.println("Request Headers");
//3.Request Headers
Enumration e = req.getHeaderNames();
while (e.hasMoreElements()) {
String hn = e.nextElement().toString();
String hv = req.getHeader(hn);
out.println("<br>" + hn + ":" + hv);
}
out.println("<br>");
out.println("Loacal info");
//4. Locals supported by Browser
out.println("<br>req.getLocal():" +
req.getLocale());
out.println("<br>");
out.println("Other Info");
//5. Other information from
Requestout.println("<br>Method:" +
req.getMethod());
out.println("<br>RequestURI:" +
req.getRequestURI());
out.println("<br>RequestURL:" +
req.getRequestURL());
out.println("<br>Protocol:" +
req.getProtocol());
out.println("<br>ContentLength:" +
req.getContentLength());
out.println("<br>ContentType:" + req.getConte ntType());
out.println("<br>RemoteAddr:" + req.getRemoteA ddr());
out.println("<br>RemotePort:" + req.getRemoteP ort());
out.println("<br>RemoteHost:" + req.getRemoteH ost());
out.println("<br>ServerPort:" + req.getServerP ort());
out.println("<br>ServerName:" + req.getServerN ame());
out.println("<br>QueryString:" + req.getQueryS tring());
out.println("<br>ServletPath:" + req.getServle tPath());
out.println("<br>ContextPath:" + req.getContex tPath());
}
}
3. web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchemainstance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/webapp_3_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0">
<display-name>Jtc14</display-name>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>TestServlet</servlet-name>
<servletclass>com.jtcindia.servlet.TestServlet</servletclass>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>TestServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/test.jtc</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
• Create Devlopment Directory Structure
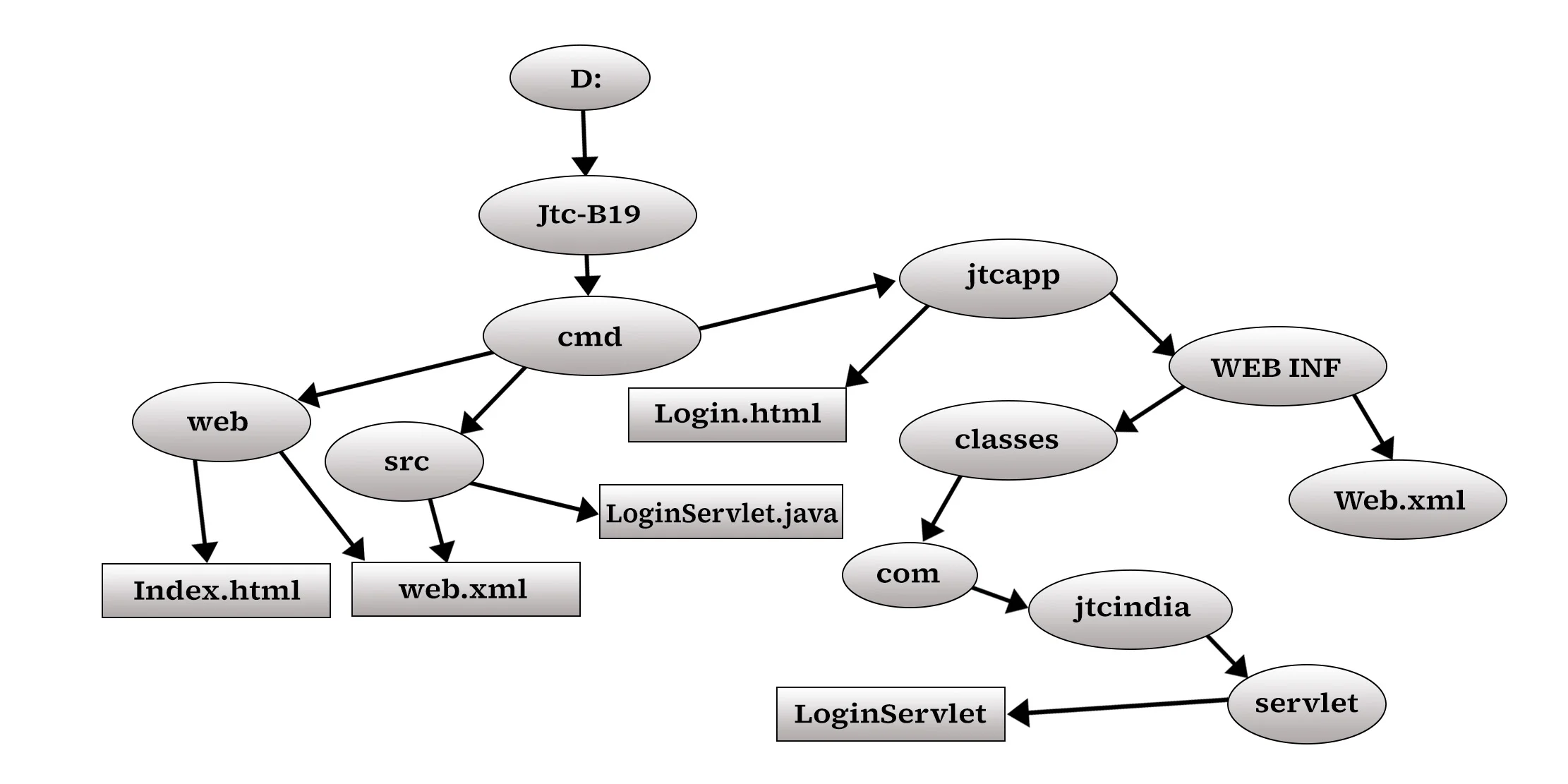
• Use any text editor to create the required file.
• You need to set the class path for servlet-api.jar to compile your servlet class.
o servlet-api.jar file is available in E:Tomcat 6.0lib.
o Set CLASSPATH=%CLASSPATH%;E:Tomcat 6.0libServlet-api.jar;
• After compiling, you will get the class files.
• Create the development directory structure and copy the files to the required directory.
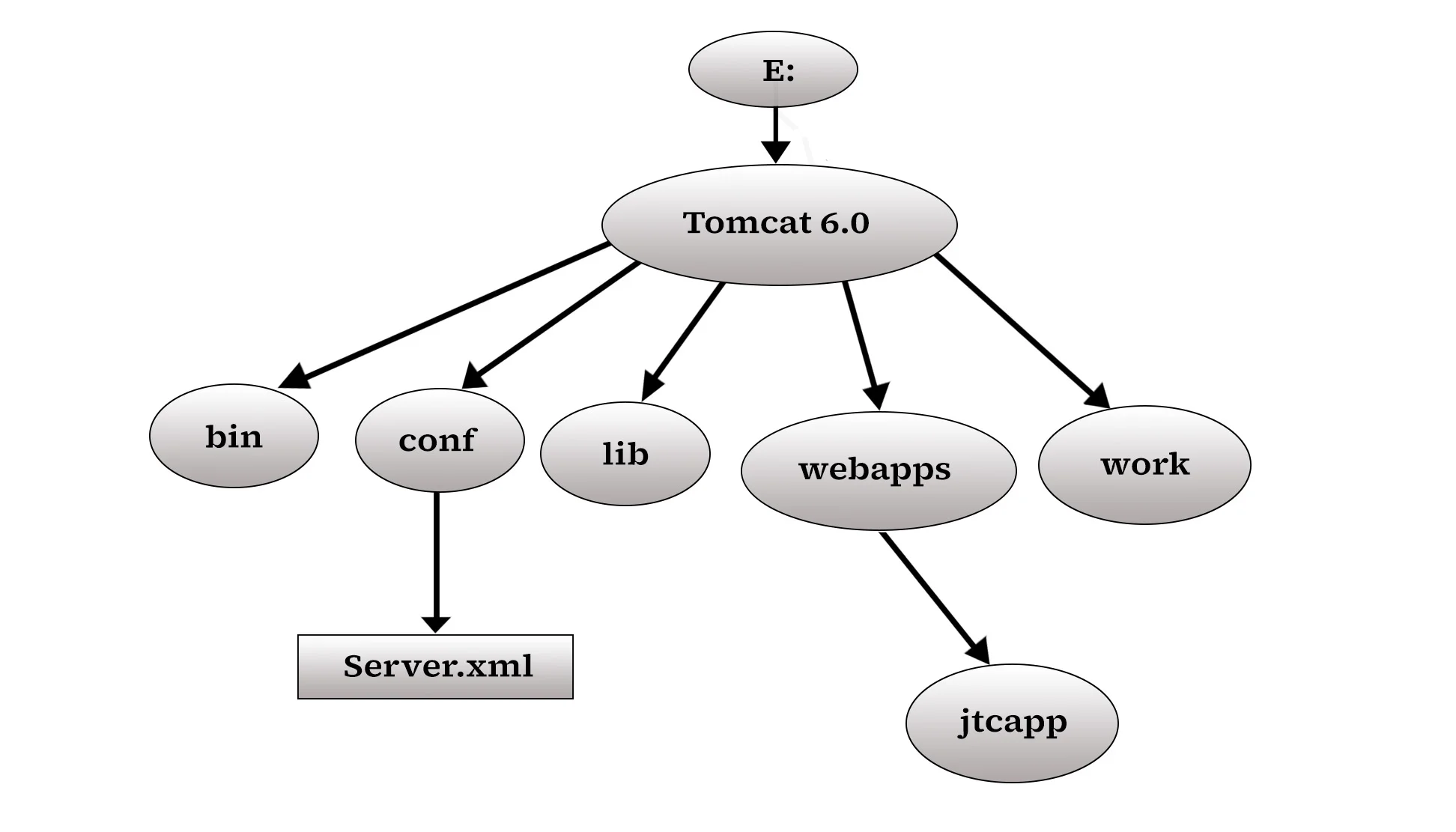
• Copy the application to E:Tomcat 6.0. webapp directory.
• Start the server from outside the eclipse.
• Using a web browser, test your application.
http://localhost:9999/jtcapp