• CallableStatement is an interface available in java.sql package and extends PreparedStatement interface.
• You can create the CallableStatement using the following methods of Connection interface.
○ CallableStatement prepareCall(String)
○ CallableStatement prepareCall(String,int , int)
○ CallableStatement prepareCall(String,int , int, int)
• After creating the CallableStatement object , you can call one of the following methods to submit the SQL Statement to Database.
○ public int executeUpdate()
○ public boolean execute()
○ public ResultSet executeQuery()
• CallableStatement is designed mainly to invoke the stored procedures running in the database.
• Stored procedure is pre-compiled procedure .i.e. when you create the procedure then that procedure will be compiled and stored in database memory. When you make call to the procedure then that pre-compiled procedure will be executed directly.
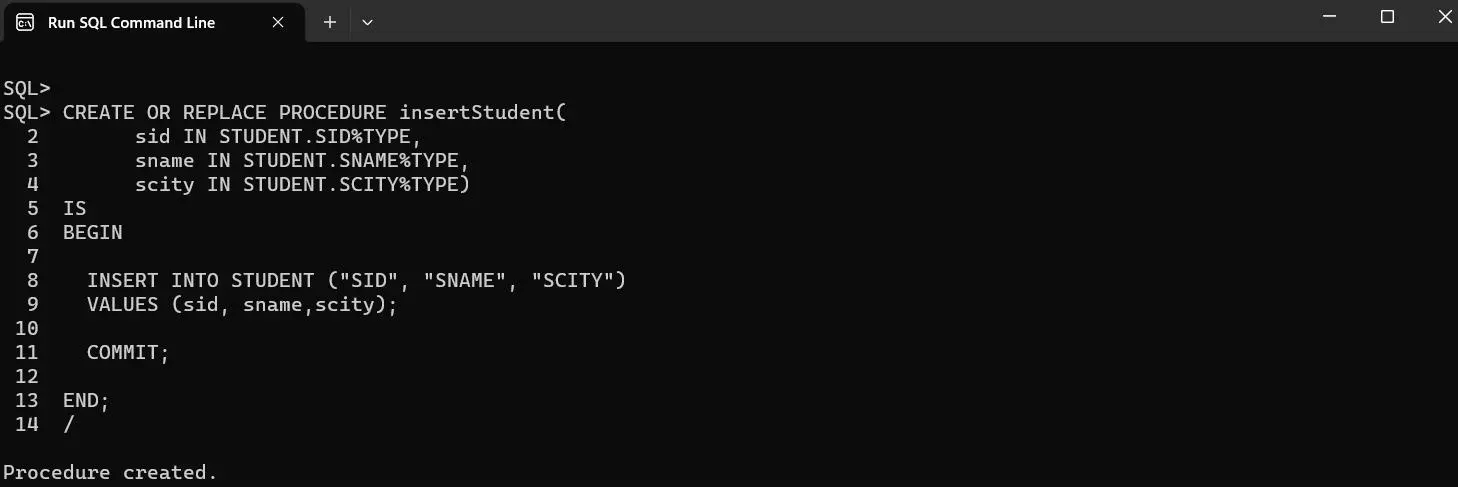
Example to create Stored Procedure for Insertion in Oracle Database.
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE insertStudent(
sid IN STUDENT.SID%TYPE,
sname IN STUDENT.SNAME%TYPE,
scity IN STUDENT.SCITY%TYPE)
IS
BEGIN
INSERT INTO STUDENT ("SID", "SNAME", "SCITY")
VALUES (sid, sname,scity);
COMMIT;
END;
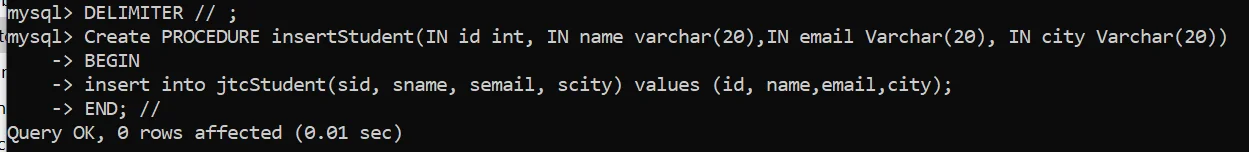
Example to create Stored Procedure for Insertion in MySQL Database.
DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS insertStudent;
DELIMITER // ;
Create PROCEDURE insertStudent(IN id int, IN name varchar(20),IN email Varchar(20), IN city Varchar(20))
BEGIN
insert into jtcStudent(sid, sname, semail, scity) values (id, name,email,city);
END; //
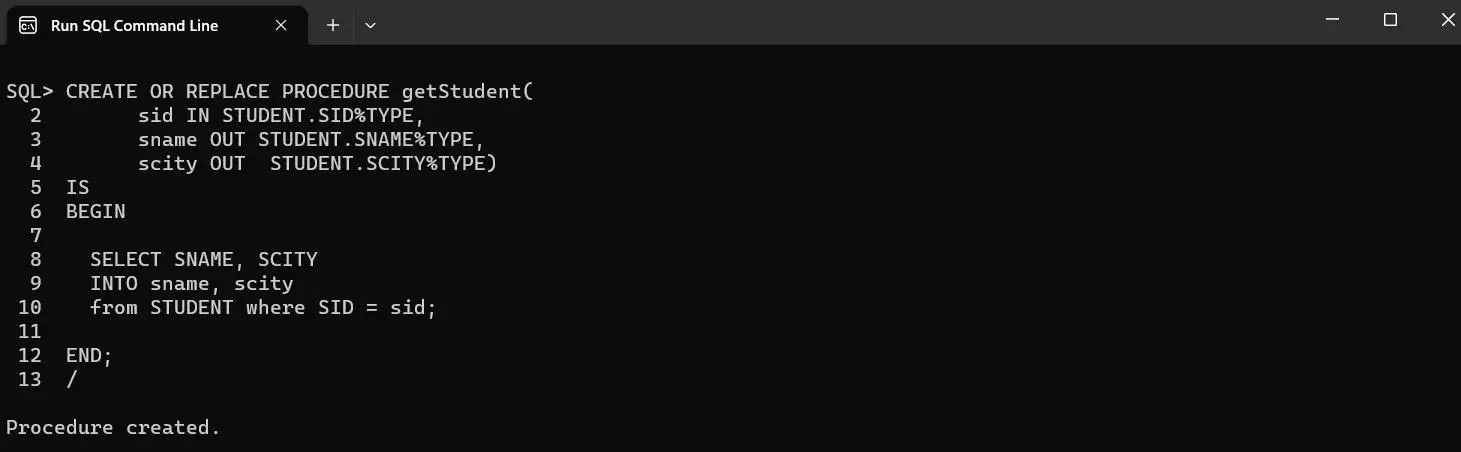
Example to create Stored Procedure for Selection in Oracle Database.
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE getStudent(
sid IN STUDENT.SID%TYPE,
sname OUT STUDENT.SNAME%TYPE,
scity OUT STUDENT.SCITY%TYPE)
IS
BEGIN
SELECT SNAME, SCITY
INTO sname, scity
from STUDENT where SID = sid;
END;
/
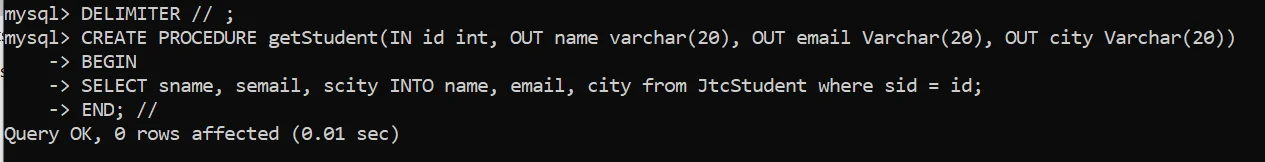
Example to create Stored Procedure for Selection in MySQL Database.
DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS getStudent;
DELIMITER // ;
CREATE PROCEDURE getStudent(IN id int, OUT name varchar(20), OUT email Varchar(20), OUT city Varchar(20))
BEGIN
SELECT sname, semail, scity INTO name, email, city from JtcStudent where sid = id;
END; //
• Using the Single CallableStatement type object, you can make a call to only one stored procedure.
• We use Stored Procedures when you want to run some logic in database.
import java.sql.CallableStatement;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Jtc8 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/tutorial;
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "root", "root");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String sql = "{call insertStudent(?,?,?,?)}";
CallableStatement statement = con.prepareCall(sql);
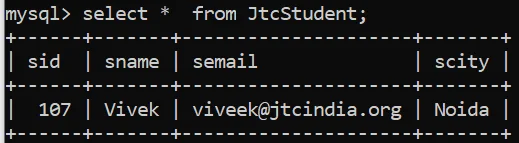
statement.setInt(1, 107);
statement.setString(2, "Vivek");
statement.setString(3, "viveek@jtcindia.org");
statement.setString(4, "Noida");
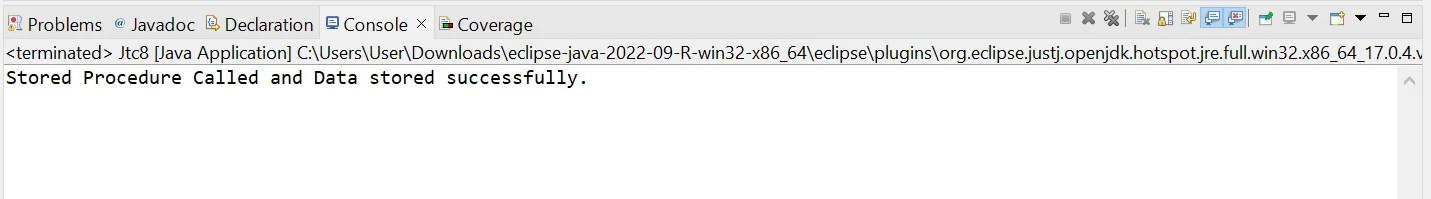
int i = statement.executeUpdate();
if (i == 1) {
System.out.println("Stored Procedure Called and Data stored successfully.");
} else {
System.out.println("Try-Again");
}
}
}
import java.sql.CallableStatement;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.sql.Types;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Jtc9 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/tutorial";
Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "root", "root");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String sql = "{call getStudent(?,?,?,?)}";
CallableStatement statement = con.prepareCall(sql);
statement.setInt(1, 107);
statement.registerOutParameter(2, Types.VARCHAR);
statement.registerOutParameter(3, Types.VARCHAR);
statement.registerOutParameter(4, Types.VARCHAR);
statement.execute();
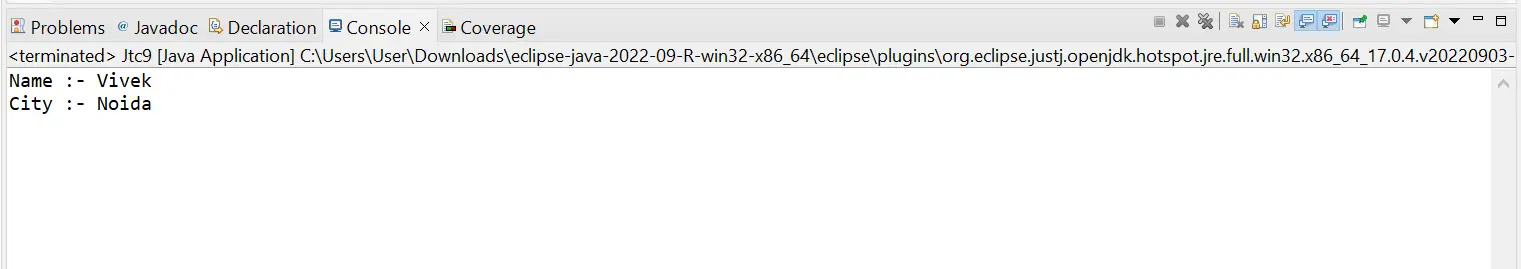
System.out.println("Name :- " + statement.getString(2));
System.out.println("City :- " + statement.getString(4));
}
}
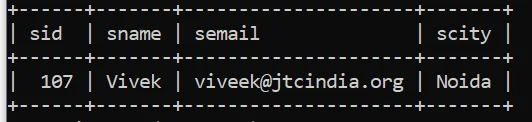
In this Example we are using java.sql.CallableStetment type object to call Stored Procedure which is dedicated to select a row from STUDENT table on the basis of sid.