Pseudo-classes
CSS pseudo-classes are special keywords used to define a specific state of an HTML element. They allow you to apply styles to elements in response to user interactions or dynamic conditions without needing to add extra classes or modify the HTML structure. Pseudo-classes are denoted by a colon (:) followed by the pseudo-class name.
Syntax:-
selector:pseudo-class {
Here are some commonly used CSS pseudo-classes:
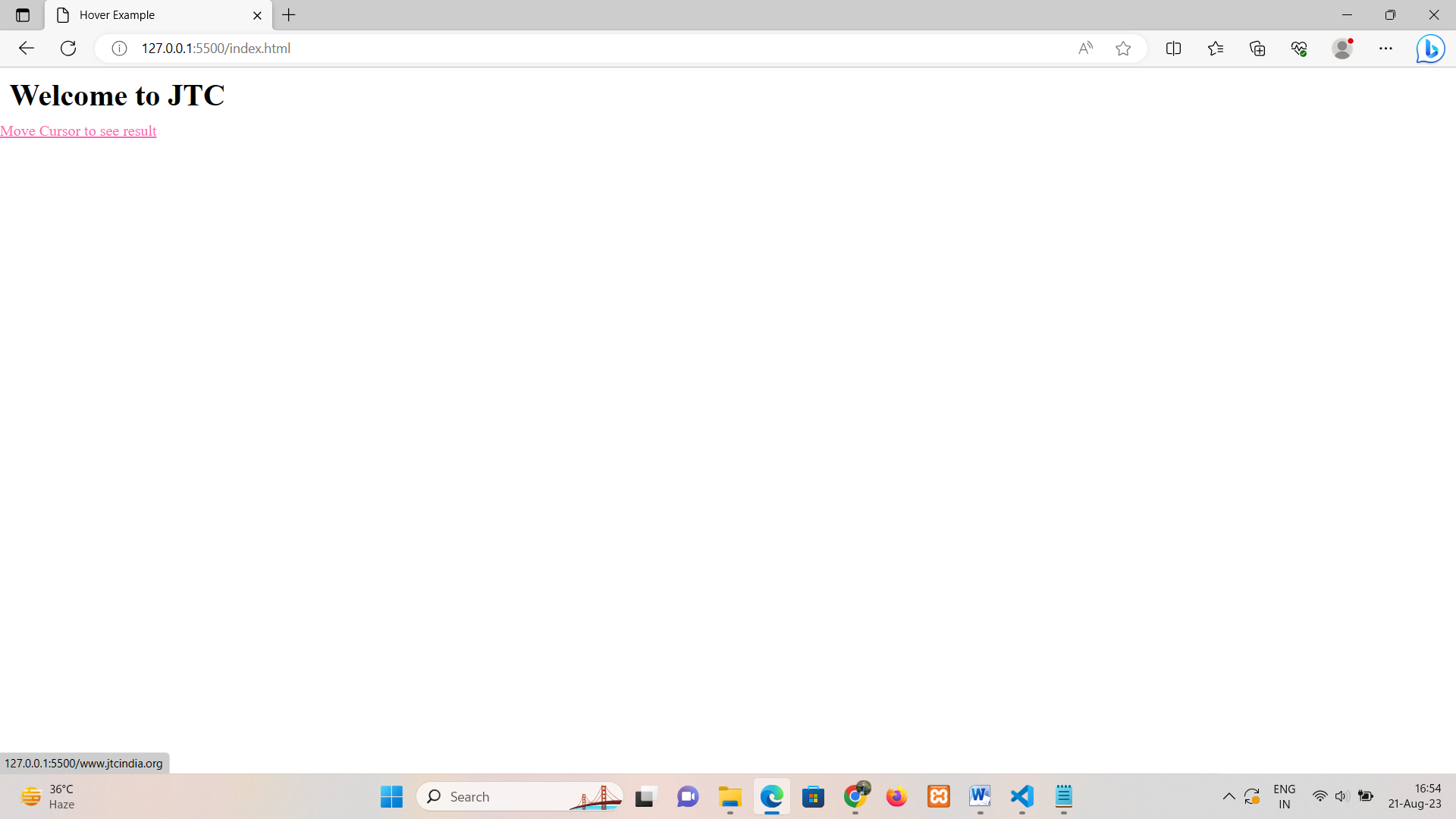
• hover: Applies styles when the mouse pointer is over the element.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
<title>Hover Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to JTC</h1>
<a href="www.jtcindia.org">Move Cursor to see result</a>
</body>
</html>
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
h1 , p{
padding: 10px;
}
a:hover{
color: hotpink;
}
Show Output
• active: Applies styles when an element is being activated (e.g., clicked).
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
<title>Active Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to JTC</h1>
<button>Click to see result</button>
</body>
</html>
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
h1 , p{
padding: 10px;
}
button:active {
background-color: #ff0000; /* Change button color when clicked */
}
Show Output
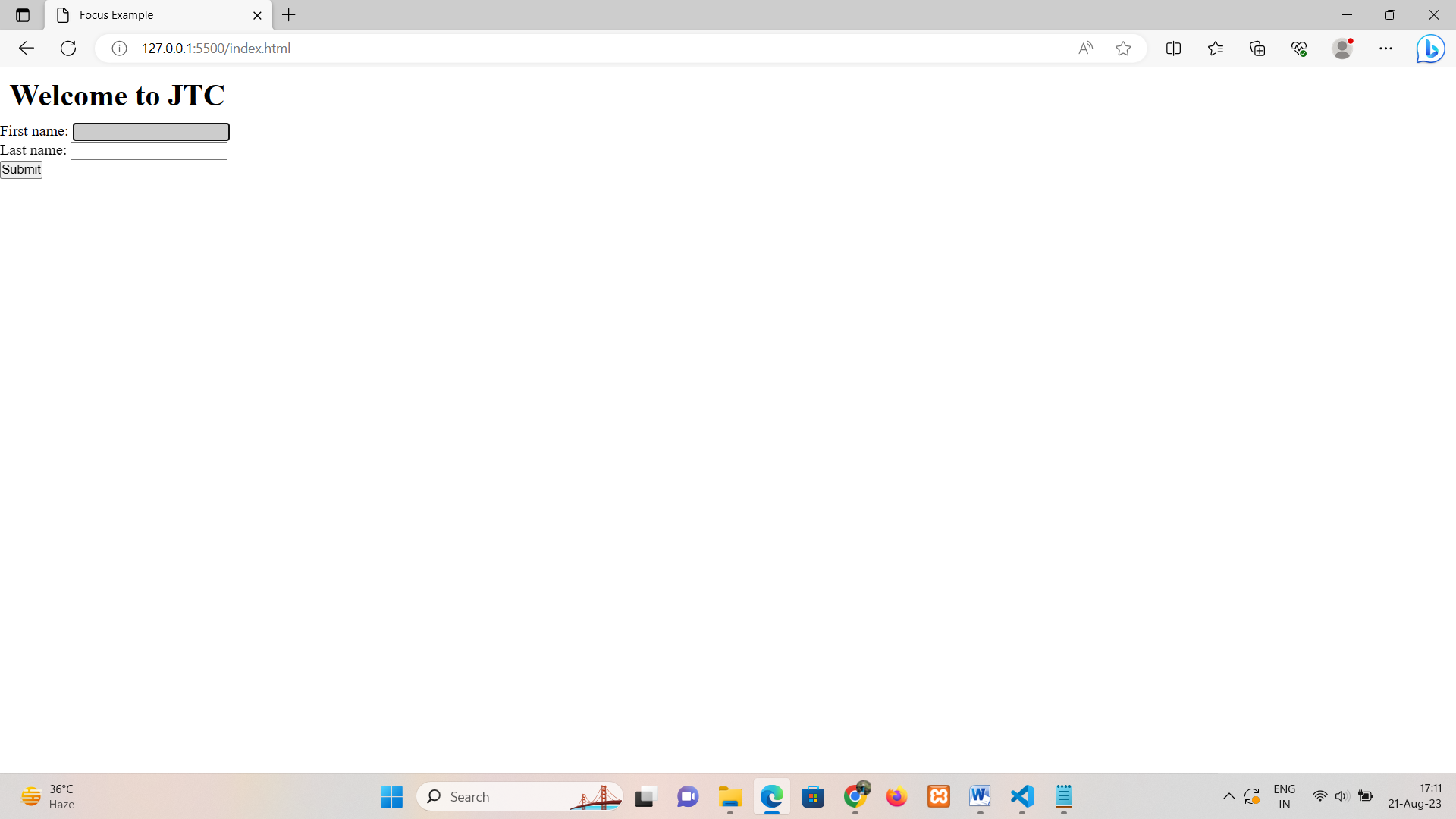
• focus: Applies styles when an element receives focus (e.g., through keyboard navigation).
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
<title>Focus Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to JTC</h1>
<form>
First name: <input type="text" name="fname"><br>
Last name: <input type="text" name="lname"><br>
<input type="submit" >
</form>
</body>
</html>
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
h1 , p{
padding: 10px;
}
input:focus {
background-color: #ccc; /* Change input color when clicked */
}
Show Output
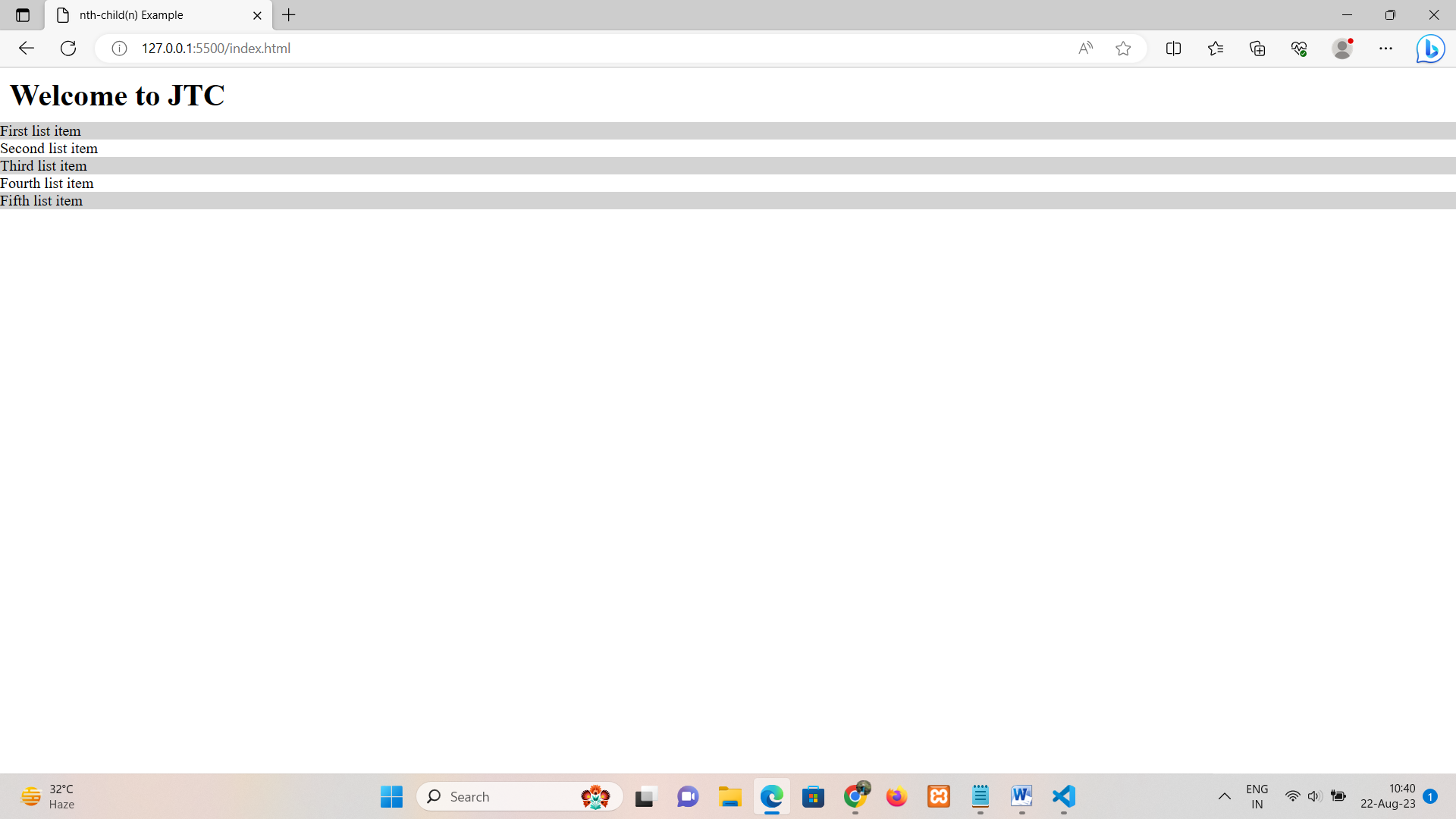
• nth-child(n): Applies styles to elements based on their position within a parent element.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
<title>nth-child(n) Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to JTC</h1>
<ul>
<li>First list item</li>
<li>Second list item</li>
<li>Third list item</li>
<li>Fourth list item</li>
<li>Fifth list item</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
h1 , p{
padding: 10px;
}
ul li:nth-child(odd) {
background-color: lightgray; /* Apply background color to odd list items */
}
Show Output
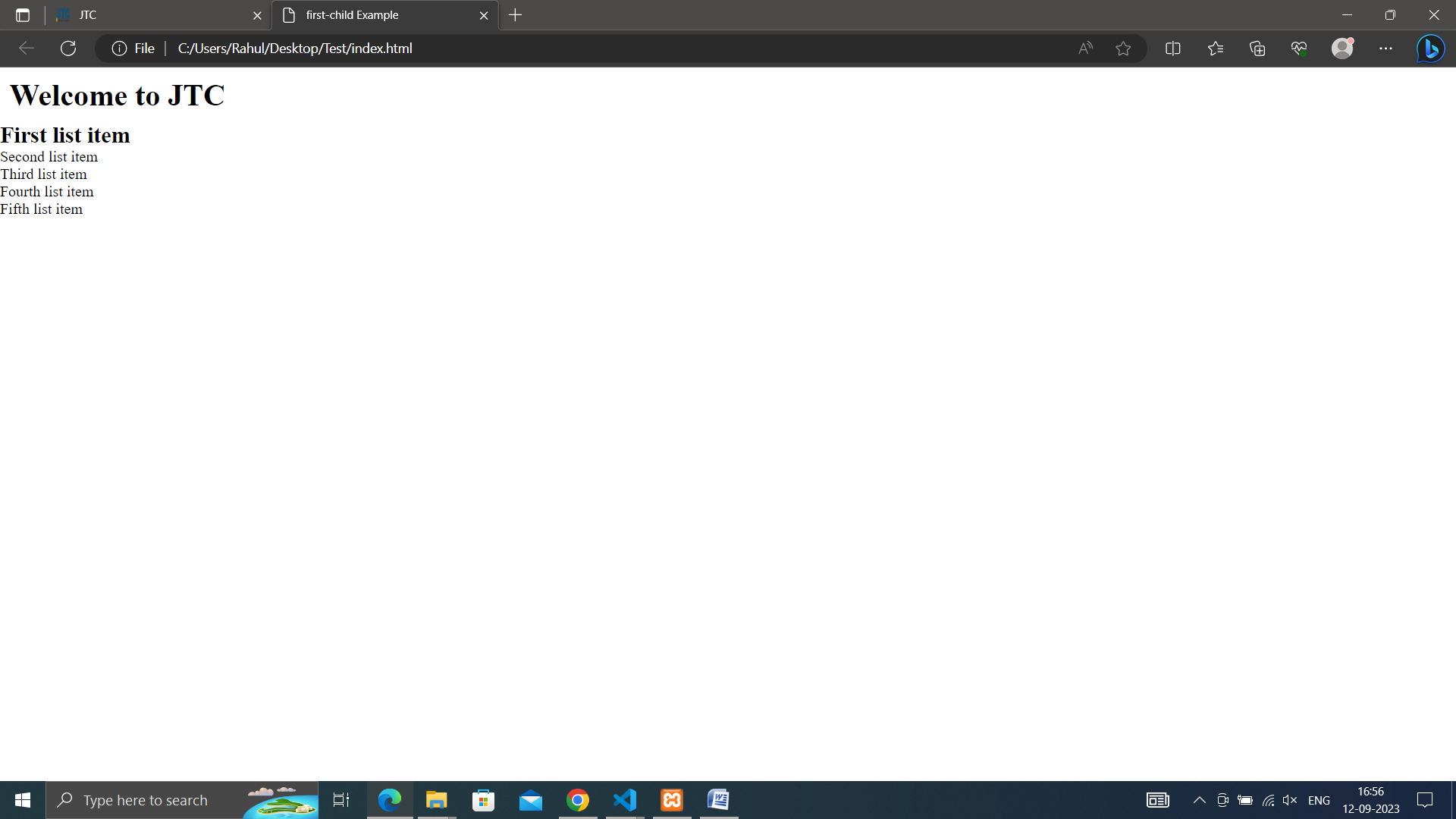
• first-child: Applies styles to the first child element of a parent.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
<title>first-child Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to JTC</h1>
<ul>
<li>First list item</li>
<li>Second list item</li>
<li>Third list item</li>
<li>Fourth list item</li>
<li>Fifth list item</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
h1 , p{
padding: 10px;
}
ul li:first-child {
font-weight: bold; /* Style the first list item differently */
font-size: 24px;
}
Show Output
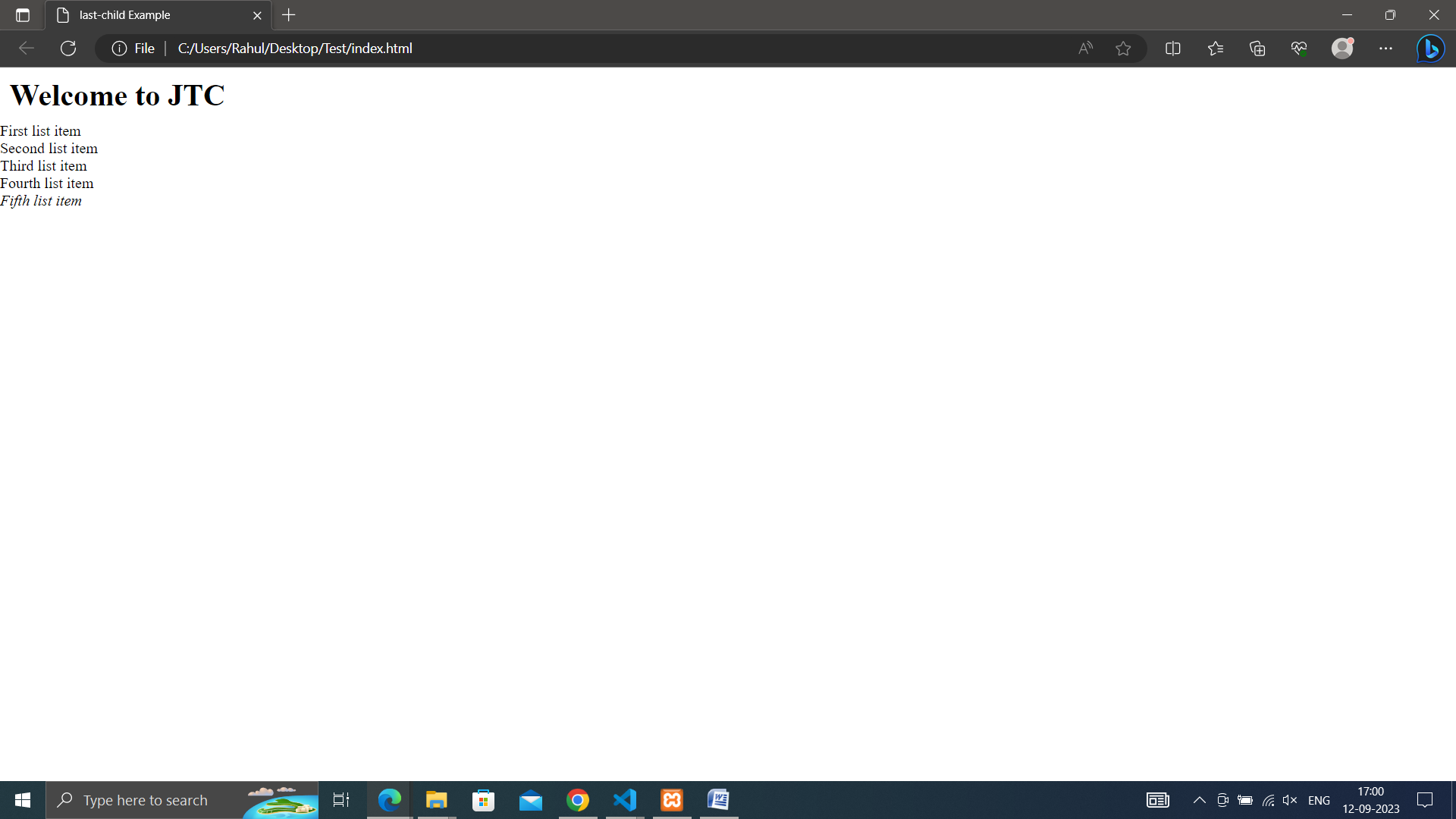
• last-child: Applies styles to the last child element of a parent.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
<title>last-child Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to JTC</h1>
<ul>
<li>First list item</li>
<li>Second list item</li>
<li>Third list item</li>
<li>Fourth list item</li>
<li>Fifth list item</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
h1 , p{
padding: 10px;
}
ul li:last-child {
font-style: italic; /* Style the last list item differently */
}
Show Output
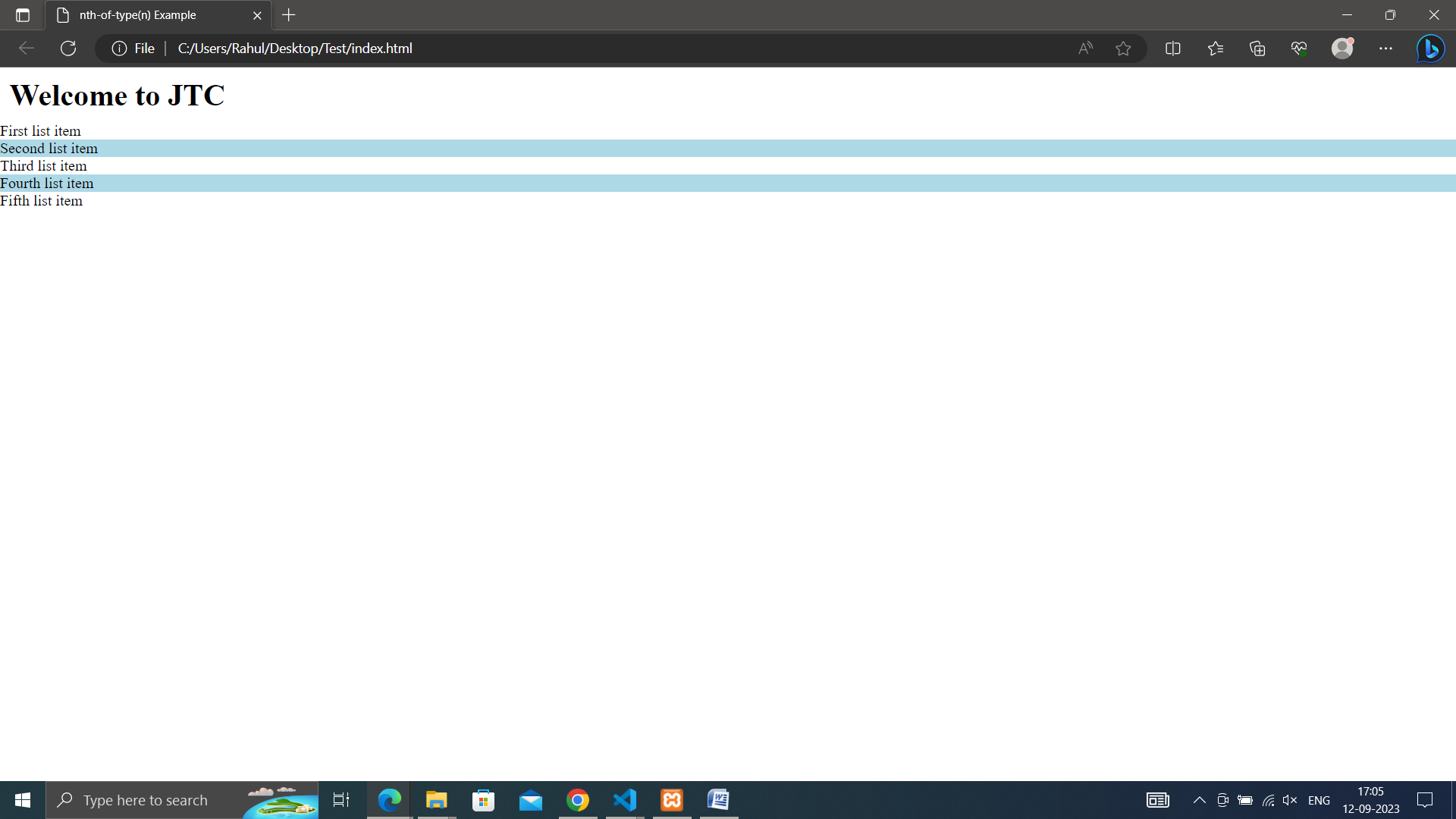
• nth-of-type(n): Applies styles to elements based on their position among elements of the same type within a parent.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
<title>nth-of-type(n) Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to JTC</h1>
<ul>
<li>First list item</li>
<li>Second list item</li>
<li>Third list item</li>
<li>Fourth list item</li>
<li>Fifth list item</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
h1 , p{
padding: 10px;
}
ul li:nth-of-type(even) {
background-color: lightblue; /* Apply background color to even list items */
}
Show Output
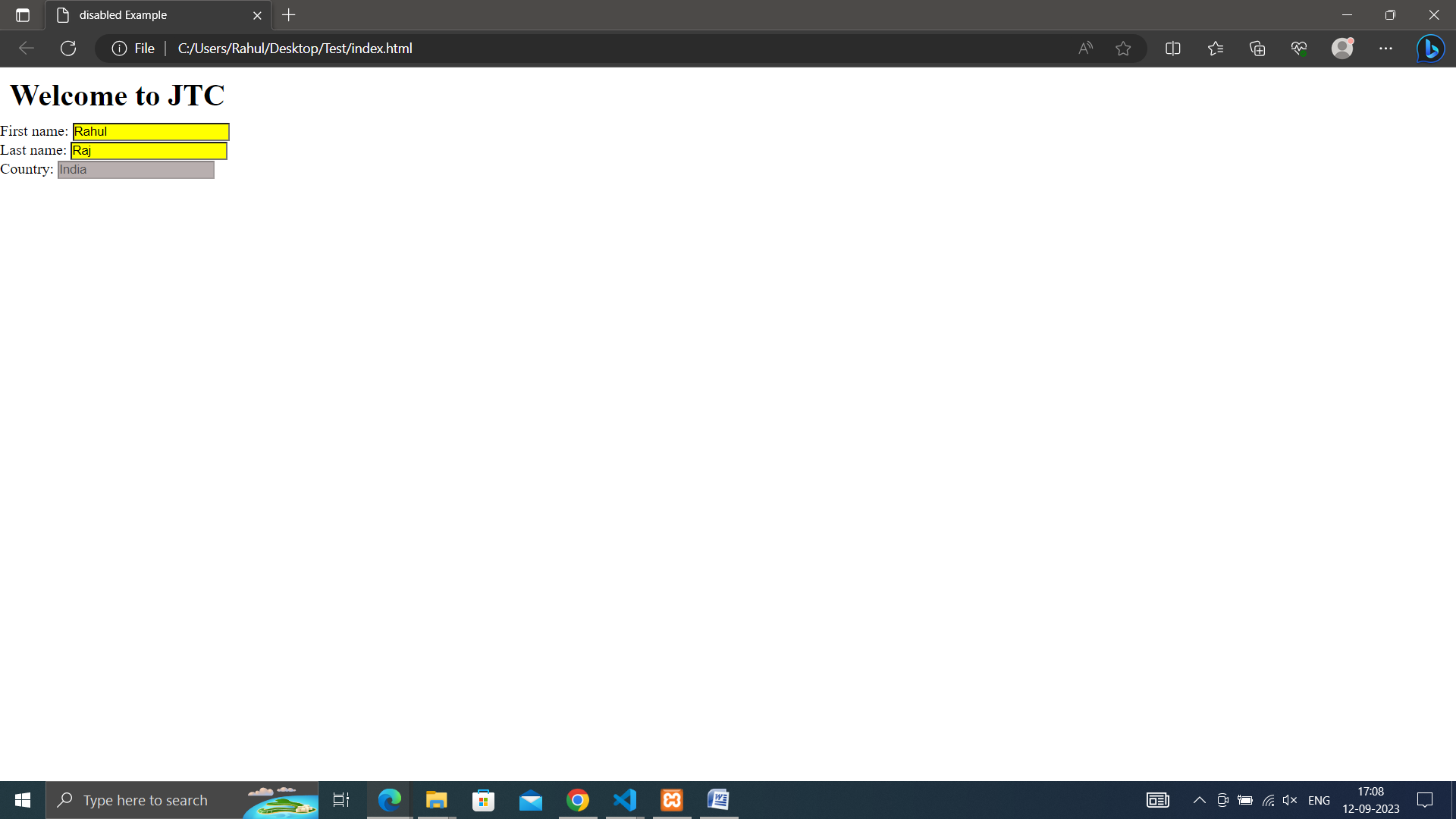
• disabled: Applies styles to disabled form elements.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport"content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="stylesheet"href="style.css">
<title>disabled Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to JTC</h1>
<form action="">
First name: <input type="text"value="Rahul"><br>
Last name: <input type="text"value="Raj"><br>
Country: <input type="text"disabled="disabled"value="India">
</form>
</body>
</html>
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
h1 , p{
padding: 10px;
}
input[type=text]:enabled {
background: #ffff00;
}
input[type=text]:disabled {
background: #dddddd;
}
Show Output